Problem
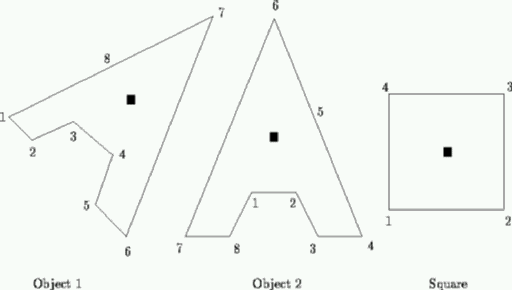
Consider objects such as these. They are polygons, specified by the coordinates of a centre of mass and their vertices. In the figure, centres of mass are shown as black squares. The vertices will be numbered consecutively anti-clockwise as shown.
An object can be rotated to stand stably if two vertices can be found that can be joined by a straight line that does not intersect the object, and, when this line is horizontal, the centre of mass lies above the line and strictly between its endpoints. There are typically many stable positions and each is defined by one of these lines known as its base line. A base line, and its associated stable position, is identified by the highest numbered vertex touched by that line.
Write a program that will determine the stable position that has the lowest numbered base line. Thus for the above objects, the desired base lines would be 6 for object 1, 6 for object 2 and 2 for the square. You may assume that the objects are possible, that is they will be represented as non self-intersecting polygons, although they may well be concave.
Input and Output
Successive lines of a data set will contain: a string of less than 20 characters identifying the object; the coordinates of the centre of mass; and the coordinates of successive points terminated by two zeroes (0 0), on one or more lines as necessary. There may be successive data sets (objects). The end of data will be defined by the string ‘#’.
Output will consist of the identification string followed by the number of the relevant base line.
Sample input
|
|
Sample output
|
|
Solution
題目描述:
給定一個多邊形,將會給予這個多邊形的質心和頂點。在圖中,質心表示成黑色正方形的小點,而頂點將會使用連續編號逆時針給點。
多邊形可以藉由旋轉放置於水平,並且穩定立起。這時可以發現,會有兩個頂點拉起的水平線,並且質心會位於水平線上的兩個端點之間。
通常一個多邊形具有多個這種水平放置方法,對於一個水平放置方式,可以用在水平線上最大編號的頂點描述。
請輸出最小水平放置的編號。
題目解法:
對多邊形著手凸包計算,這裡使用單調鍊去完成凸包。接著利用內積找到質心是否在兩個水平線端點 (segment 的上方) 之間。
可以利用外積判斷是否在線 (line) 上。
好好利用數學運算,將可以在簡短的代碼完成。
|
|